1. History, Approaches, Methods (Ch 1 & 2)
1.1 History of psychology
- What is Psychology?
- Pysche: mind, spirit, soul
- Ology: study of
- Psychology is the scientific study of human behavior and mental processes
- Structuralism
- Wilhelm Wundt
- First Psychology Lab in Leipzig, Germany in 1879
- Ideas of Structuralism
- Consciousness was made up of basic elements that were combined in different ways to produce perceptions
- Discover the basic elements of mental experiences
- Introspection
- Looking inwards to understand what is involved
- Wilhelm Wundt
- Functionalism
- Lead by William James
- Less interested in what made up mental experiences
- More interested in the processes or the functions of the human condition
- Consciousness helped people and animals to adjust to their environments
1.2. Psychological Approaches
- Biological approach
- Physiological and biochemical explanation of behavior
- Genes, neurotransmitters, neurochemicals
- Behavioral approach
- Ideas
- Learned responses to predictable patterns of external stimuli
- People's behaviour is based on the environment
- Classical conditioning (Ivan Pavlov)
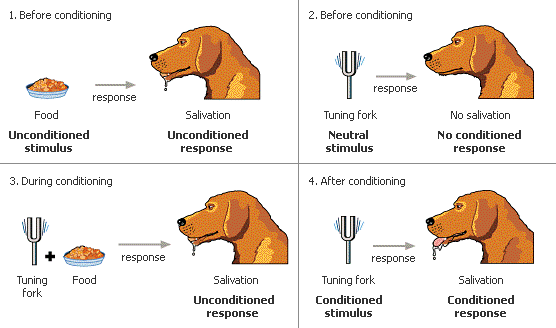
- Operant conditioning (BF Skinner)
- How rewards and punishments affect behaviors
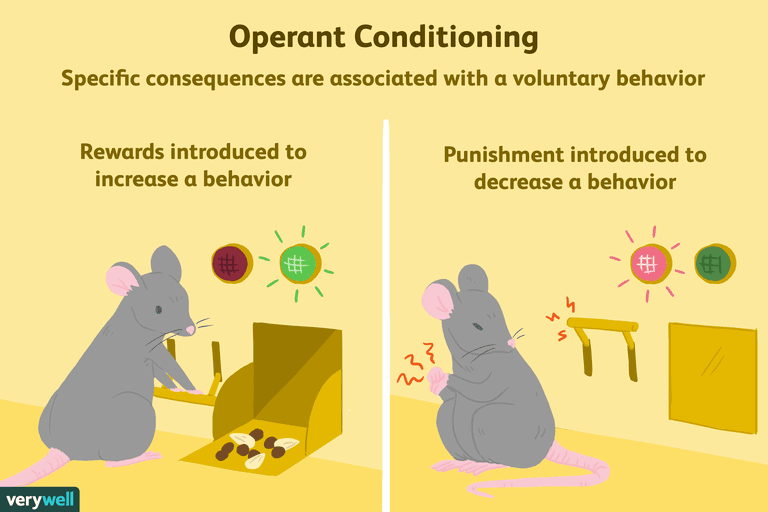
- How rewards and punishments affect behaviors
- Ideas
- Psychodynamic approach (Sigmund Freud)
- Ideas
- Unmet needs/unresolved conflicts from childhood determine personality
- Behavior as a result of unconscious, attachment and interpersonal connection
- Parts of psyche
- Id: I want it, and I want it now
- Ego:Moderator between id and superego. Reality Principle
- Superego: Moral
- Defense mechanisms
- Sexual and aggressive urges drive behavior, thoughts and feelings
- Ideas
- Cognitive approach
- In reaction to behaviorism (focused on observable events)
- Behavior as a result of “expectations”, “feelings” and “thoughts”
- Study problem solving, attention, memory and other thought processes
- Humanistic approach
- Ideas
- Developed in reaction to Behaviorist and Psychodynamic models
- People are motivated by desire for growth and development
- We have free will, and we are motivated to grow
- Abraham Maslow
- Self actualization
- Hierarchy of Needs
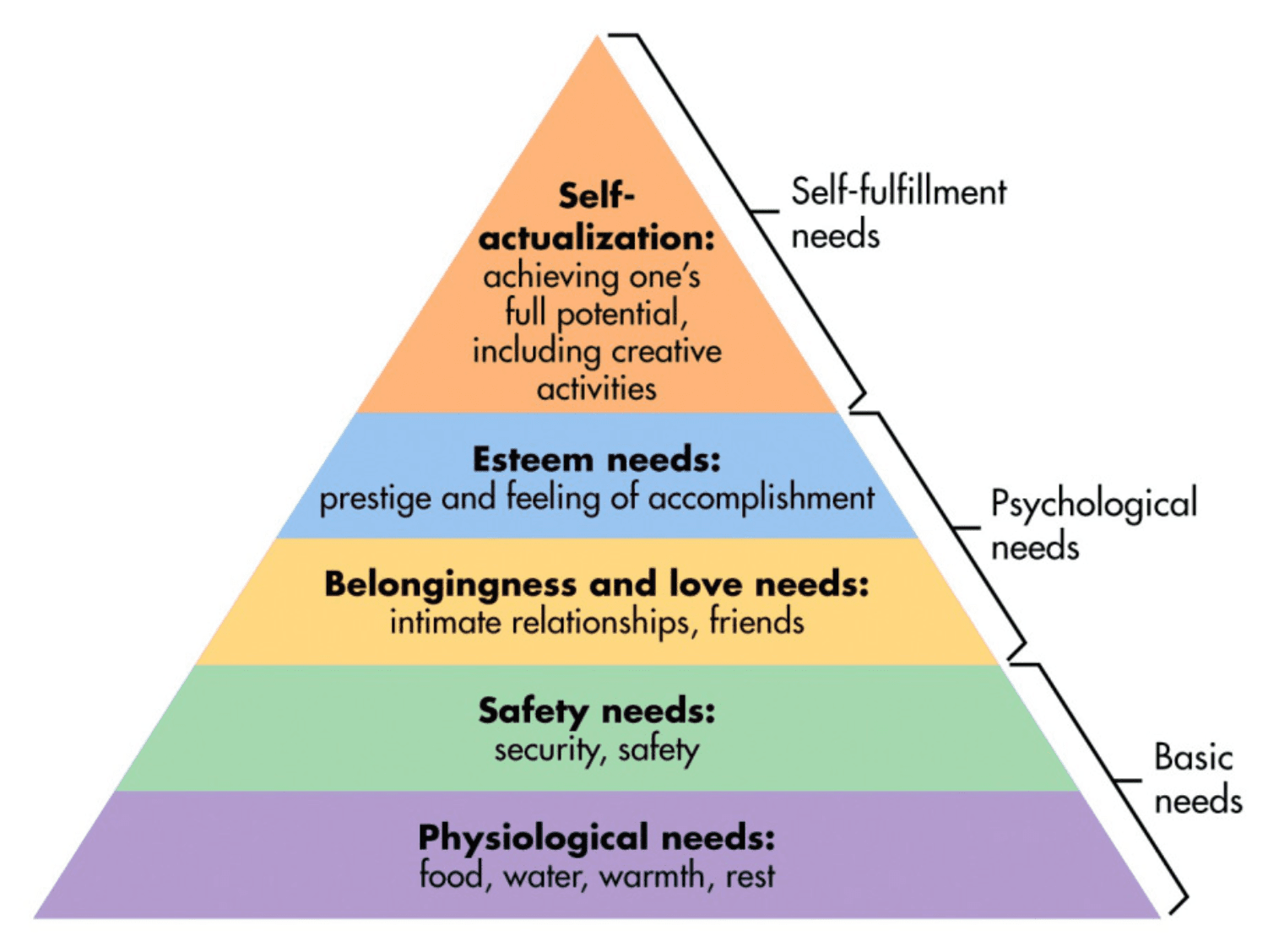
- Carl Rogers
- People are basically good
- Driven by unconditional positive regard
- Ideas
1.3. Research Methods
- Experimental
- Cause and effect relationship between two or more variables
- Types of variables
- Independent variable
- The variable being manipulated
- The “cause"
- Dependent variable
- The variable being measured for change
- The “effect”
- Independent variable
- Groups
- Experimental group
- Exposed to the “cause”
- Receives the independent variable
- Control group
- Not exposed to the “cause”
- Receives no treatment or some treatment that should have no effect
- Experimental group
- Methods
- Random Assignment
- Randomly choose who goes into each group
- Decrease bias
- Blind and Double Blind Study
- Neither party knows what they are receiving
- Leads to a more pure research study
- Placebo and Placebo Effect
- The sheer belief that I'm taking a medicine will change people's state of mind
- Random Assignment
- Clinical
- Case studies
- Freud used this method to develop psychoanalytic theory
- Hard to apply to a boader population
- Naturalistic observation
- Observe the behaviours of our subjects in a naturalistic environment
- Agreement among observers
- Clinical interviews
- Inter-rater reliability
- Case studies
- Correlational
- Ideas
- How two variables relate to one another
- No manipulation of variables
- Does NOT measure cause and effect
- Correlation Coefficient
- A number from -1 to 1
- Positive Correlation: Correlation Coefficient > 0
- Negative Correlation: Correlation Coefficient < 0
- Ideas
- Surveys
- Self-reporting surveys: Subject to bias
1.4. Ethics in Research
- Participants must be treated morally and respectfully
- Clearly state the purpose, duration and process of study
- Any possible harm or adverse effects should be disclosed
Quiz
The science of psychology is typically dated from the establishment of the late-nineteenthcentury Leipzig laboratory of
- (A) Hermann Ebbinghaus
- (B) Hermann von Helmholtz
- (C) William James
- (D) Wilhelm Wundt
- (E) John Locke
The behavioral research perspective is similar to the sociocultural research perspective because both focus on how behavior and mental processes are explained by
- (A) internal factors such as genes
- (B) the external environment
- (C) memory systems
- (D) evolution
- (E) problem-solving skills and reasoning
Which of the following types of research design is most appropriate for establishing a cause-andeffect relationship between two variables?
- (A) Correlational
- (B) Naturalistic observation
- (C) Participant observation
- (D) Experimental
- (E) Case study
Frequency theory and place theory attempt to explain how the inner ear registers the pitch of sound.
Which statement best reflects current opinion about frequency theory and place theory?
- (A) Evidence strongly supports frequency theory
- (B) Evidence strongly supports place theory.
- (C) Place theory explains the perception of complex sounds well, whereas frequency theory explains the perception of simple sounds well.
- (D) Place theory explains the perception of high-frequency sounds well, and frequency theory explains the perception of low-frequency sounds well.
- (E) There is little evidence to support either theory
The requirement that prospective participants know the general nature of a study so that they can decide whether to participate is a major part of
- (A) reciprocal determinism
- (B) confidentiality
- (C) informed consent
- (D) duty to inform
- (E) debriefing